Contents |
teaching in general
teaching_philosophy
lecture notes continnum mechanics - linear (download)
lecture notes finite element method - linear (download)
lecture notes finite element method - nonlinear (download)
current courses
me 337 - mechanics of growth
tue thu 3:15-4:30
mc cullough 126
goals
in contrast to traditional engineering structures living structures show the fascinating ability to grow and adapt their form, shape and microstructure to a given mechanical environment. this course addresses the phenomenon of growth on a theoretical and computational level and applies the resulting theories to classical biomechanical problems like bone remodeling, hip replacement, wound healing, atherosclerosis or in stent restenosis. this course will illustrate how classical engineering concepts like continuum mechanics, thermodynamics or finite element modeling have to be rephrased in the context of growth. having attended this course, you will be able to develop your own problem-specific finite element based numerical solution techniques and interpret the results of biomechanical simulations with the ultimate goal of improving your understanding of the complex interplay between form and function.
syllabus
| day | date | topic | slides | homework | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tue | apr | 03 | introduction - different forms of growth | s01 | h01 wiki growth |
| thu | apr | 05 | rep tensor calculus - tensor algebra | s02 | |
| tue | apr | 10 | rep tensor calculus - tensor analysis | s03 | h02 tensors |
| thu | apr | 12 | kinematic equations | s04 | |
| tue | apr | 17 | balance equations – closed systems | s05 | |
| thu | apr | 19 | balance equations – open systems | s06 | example rocket propulsion |
| tue | apr | 24 | constitutive equations – density growth | s07 | example astronaut |
| thu | apr | 26 | constitutive equations – volume growth | s08 | example tumor growth |
| tue | mai | 01 | finite element method – density growth theory | s09 | |
| thu | mai | 03 | finite element method – density growth matlab | s10 | matlab density |
| tue | mai | 08 | examples – density growth | s11 | example bone |
| thu | mai | 10 | finite element method – density growth alternative | s12 | |
| tue | mai | 15 | examples - volume growth | s13 | |
| thu | mai | 17 | no class / visit of thor besier's lab on mai 21st | ||
| tue | mai | 22 | project discussion | ||
| thu | mai | 24 | examples - remodeling | s16 | h03 wiki growth |
| tue | mai | 29 | finite element method - volume growth theory | ||
| thu | mai | 31 | finite element method – volume growth matlab | ||
| tue | jun | 05 | example – atherosclerosis, in stent restenosis | ||
| thu | jun | 07 | wiki session – vote on articles |
matlab files
voila!... just to get used to tensor notation and matlab
matlab_ex01.m ... the one with all the tensors
finally... here's the matlab nonlinear finite element code for density growth in bone!
matlab_bone.tar ... the one where u got it all
or... if you prefer to look @all the individual files
i've tried to put comments to most of the variables, drop me an email if you want moooore ;-)
assm_sys.m ... the one with the strange big A operator
cnst_grw.m ... the one with the constitutive equations for growth
element1.m ... the one with the element residual and tangent
ex_frame.m ... the one with the example of the frame structure
ex_unity.m ... the one with the example of two elements
extr_dof.m ... the one which extracts element information from the global field
mesh_sqr.m ... the one which meshes a square domain
nlin_fem.m ... the one and only
plot_int.m ... the one to plot internal variables on the spatial/deformed configuration
plot_mat.m ... the one to plot the material/undeformed configuration
res_norm.m ... the one which tells you how far you are away from your ultimate goal
solve_nr.m ... the one with the solution to all problems
upd_dens.m ... the one with yet another newton iteration to calculate the density
bone example
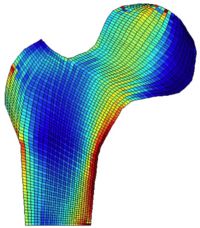
| for those of you who are interested in calculating the bone example from the literature (2) and (3), bex converted the bone file (you're awesome! thanx!) and now you could all run the bone with matlab! just download the gzipped archive above, unpack it, call the main file nlin_fem and type step,,50 to run 50 time steps to allow for density redistribution. you should then obtain the figure on the left... just throw me an email if it doesn't work! ... yes, i know... the code's slow... so go'n get a cup of coffee... or try to re-code cnst_grw.m in terms of either spatial or material stresses & tangents by using voigt's matrix notation and speed up element1.m by using the traditional old-fashioned b-operator, it's maybe ugly in the code but a loaaad faster! |
additional reading
don't feel forced to read all of this! it's just additional information that some of you might want to look at!
(1) taber l: biomechanics of growth, remodeling, and morphogenesis, appl mech rew 48, 487-545, 1995
(2) jacobs, cr, levenston me, beaupre gs, simo jc, carter dr: numerical instabilities in bone remodeling simulations: the advantages of a node-based finite element approach, j biomechanics 28, 449-459, 1995
(3) kuhl e, menzel a, steinmann p: computational modeling of growth - a critical review, a classification and two new consistent approaches, computational mechanics 32, 71-88, 2003
(4) rodriguez ek, hoger a, mc culloch a: stress-dependent finite growth in soft elastic tissues, j biomechanics 27, 455-467, 1994
(5) kuhl e, maas r, himpel g, menzel a: computational modeling of arterial wall growth - attempts towards patient-specific simulations based on computer tomography, biomech model mechanobiol, available online first, DOI 10.1007/s10237-006-0062-x
density studies in tennisplayers
p01
p02
p03
p04 rebecca taylor
more tennisplayers
p05
p06
p07
p08
p09
p10
p11
p12
p13
p14 chun hua zheng
more tennisplayers
p15
p16
p17
p18
p19
p20 julia chen
sophisticated growth law
p01 joey doll
microgrowth
p01 amir shamloo