Contents |
winter 15 - me337 - mechanics of growth
|
me 337 - mechanics of growth 15 ellen kuhl office hours thu 3:00-4:00, durand 247 winter 2015 |
goals
in contrast to traditional engineering structures living structures show the fascinating ability to grow and adapt their form, shape and microstructure to a given mechanical environment. this course addresses the phenomenon of growth on a theoretical and computational level and applies the resulting theories to classical biomechanical problems like bone remodeling, hip replacement, wound healing, atherosclerosis or in stent restenosis. this course will illustrate how classical engineering concepts like continuum mechanics, thermodynamics or finite element modeling have to be rephrased in the context of growth. having attended this course, you will be able to develop your own problem-specific finite element based numerical solution techniques and interpret the results of biomechanical simulations with the ultimate goal of improving your understanding of the complex interplay between form and function.
journal club
mechanics of growth on imechanica
class papers
zöllner am, pok jm, mcwalter ej, gold ge, kuhl e. on high heels and short muscles: a multiscale model for sarcomere loss in the gastrocnemius muscle. j theor bio, 2015;365:301–310. (download)
eskandari m, pfaller mr, kuhl e. on the role of mechanics in chronic lung disease. materials, 2013;6:5639-5658. (download) (open access)
zöllner am, abilez oj, böl m, kuhl e. stretching skeletal muscle - chronic muscle lengthening through sarcomerogenesis. plos one, 2012;7(10):e45661. (download) (open access)
pang h, shiwalkar ap, madormo cm, taylor re, andriacchi tp, kuhl e. computational modeling of bone density profiles in response to gait: a subject-specific approach. biomech model mechanobio, 2012;11:379-390. (download)
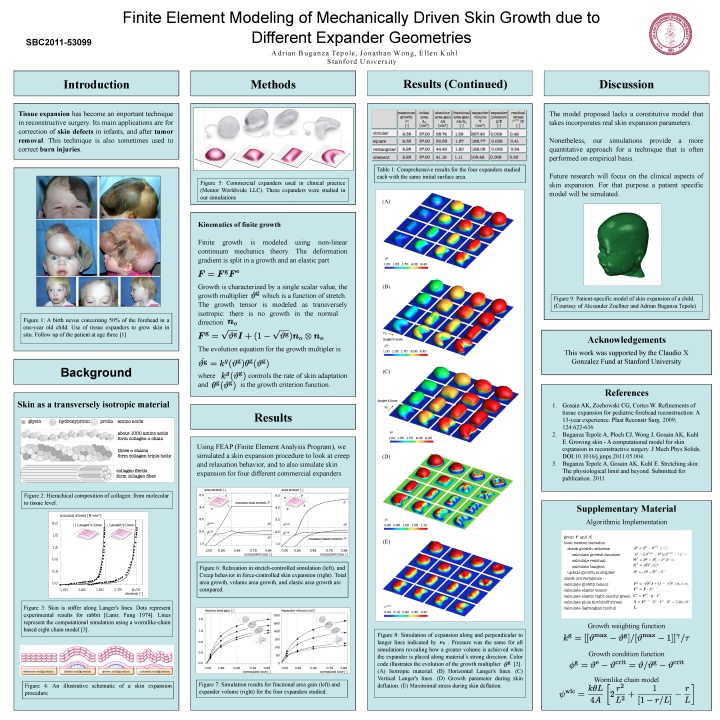
buganza tepole a, ploch cj, wong j, gosain ak, kuhl e. growing skin - a computational model for skin expansion in reconstructive surgery. j mech phys solids, 2011;59:2177-2190. (download)
taylor re, zheng ch, jackson pr, doll jc, chen jc, holzbaur krs, besier t, kuhl e. the phenomenon of twisted growth: humeral torsion in dominant arms of high performance tennis players. comp meth biomech biomed eng, 2009;12:83-93. (download)
grading
- 30 % homework - 3 homework assignments, 10% each
- 30 % midterm - closed book, closed notes, one single page cheat sheet
- 20 % final project oral presentations - graded by the class
- 20 % final project essay - graded by instructor
syllabus
| day | date | topic | slides | homework | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tue | jan | 06 | motivation - everything grows! | s01 | |
| thu | jan | 08 | basics maths - notation and tensors | s02 | |
| tue | jan | 13 | basic kinematics - large deformation and growth | s03 | h01 |
| thu | jan | 15 | kinematics - growing hearts | s04 | |
| tue | jan | 20 | project example - growing skin | s05 | |
| thu | jan | 22 | kinematics - growing brains | s06 | |
| tue | jan | 27 | balance equations - closed and open systems | s07 | |
| thu | jan | 29 | basic constitutive equations - growing muscle | s08 | h02 |
| tue | feb | 03 | basic constitutive equations - growing tumors | s09 | |
| thu | feb | 05 | volume growth - finite elements for growth | s10 | |
| tue | feb | 10 | volume growth - arteries | s11 | |
| thu | feb | 12 | project example - airway wall remodeling | s12 | |
| tue | feb | 17 | basic constitutive equations - growing bones | s13 | |
| thu | feb | 19 | density growth - finite elements for growth | s14 | h03 |
| tue | feb | 24 | density growth - growing wounds | s15 | |
| thu | feb | 26 | everything grows! - midterm summary | s16 | |
| tue | mar | 03 | midterm | ||
| thu | mar | 05 | volume growth - growing hearts | s18 | |
| tue | mar | 10 | class projects - discussion, presentation, evaluation | s19 | h04 |
| thu | mar | 12 | class projects - discussion, presentation, evaluation | ||
| fri | mar | 13 | final project reports due |
final project
buganza a, wong j, kuhl e. computational modeling of mechanically driven skin growth due to different expander geometries, farmington, pennsylvania, 2011
matlab files
finally... here's the matlab code for growth
additional reading
(1) taber l. biomechanics of growth, remodeling, and morphogenesis, appl mech rew 48, 487-545, 1995
(2) kuhl e, menzel a, steinmann p. computational modeling of growth - a critical review, a classification and two new consistent approaches, computational mechanics 32, 71-88, 2003
(3) rodriguez ek, hoger a, mc culloch a. stress-dependent finite growth in soft elastic tissues, j biomechanics 27, 455-467, 1994
(4) kuhl e, maas r, himpel g, menzel a. computational modeling of arterial wall growth - attempts towards patient-specific simulations based on computer tomography, biomech model mechanobio 6, 321-331, 2007
(5) göktepe s, abilez oj, parker kk, kuhl e. a multiscale model for eccentric and concentric cardiac growth
through sarcomerogenesis.j theor bio 265: 433-442, 2010
(6) ambrosi d, ateshian ga, arruda em, cowin sc, dumais j, goriely a, holzapfel ga, humphrey jd, kemkemer r, kuhl e, olberding je, taber la, garikipati k. perspectives on biological growth and remodeling.j mech phys solids 59: 863-883, 2011
(7)
zöllner am, buganza tepole A, kuhl e. on the biomechanics and mechanobiology of growing skin. j theor bio 297, 166-175, 2012
(8) menzel a, kuhl e. frontiers in growth and remodeling. mech res comm 42,1-14, 2012